[ad_1]
Image by storyset on Freepik
In any data pipeline, the data ingested from the sources typically goes through several transformations, so much that the data consumed from the destination is widely different from the data actually ingested from the source. Data lineage provides a comprehensive way to chart the flow of data through the system—from the source to the destination—as it undergoes transformations.
In this article, we’ll learn about data lineage and its importance. We’ll also see how data lineage facilitates better data management and go over some of the tools and platforms you can use for data lineage.
Let’s get started!
Data lineage refers to the tracking and visualization of the flow and transformation of data as it moves through various stages in a data pipeline or system. It provides a detailed understanding of the origin, movement, and transformation of data within the organization’s data pipelines—allowing data professionals to trace the data’s path from its source to its destination.
Such comprehensive understanding of the data’s life cycle is helpful for organizations aiming to enhance data quality, ensure regulatory compliance, and much more.
Key Components of Data Lineage
Now let’s explore the key components we account for in data lineage:
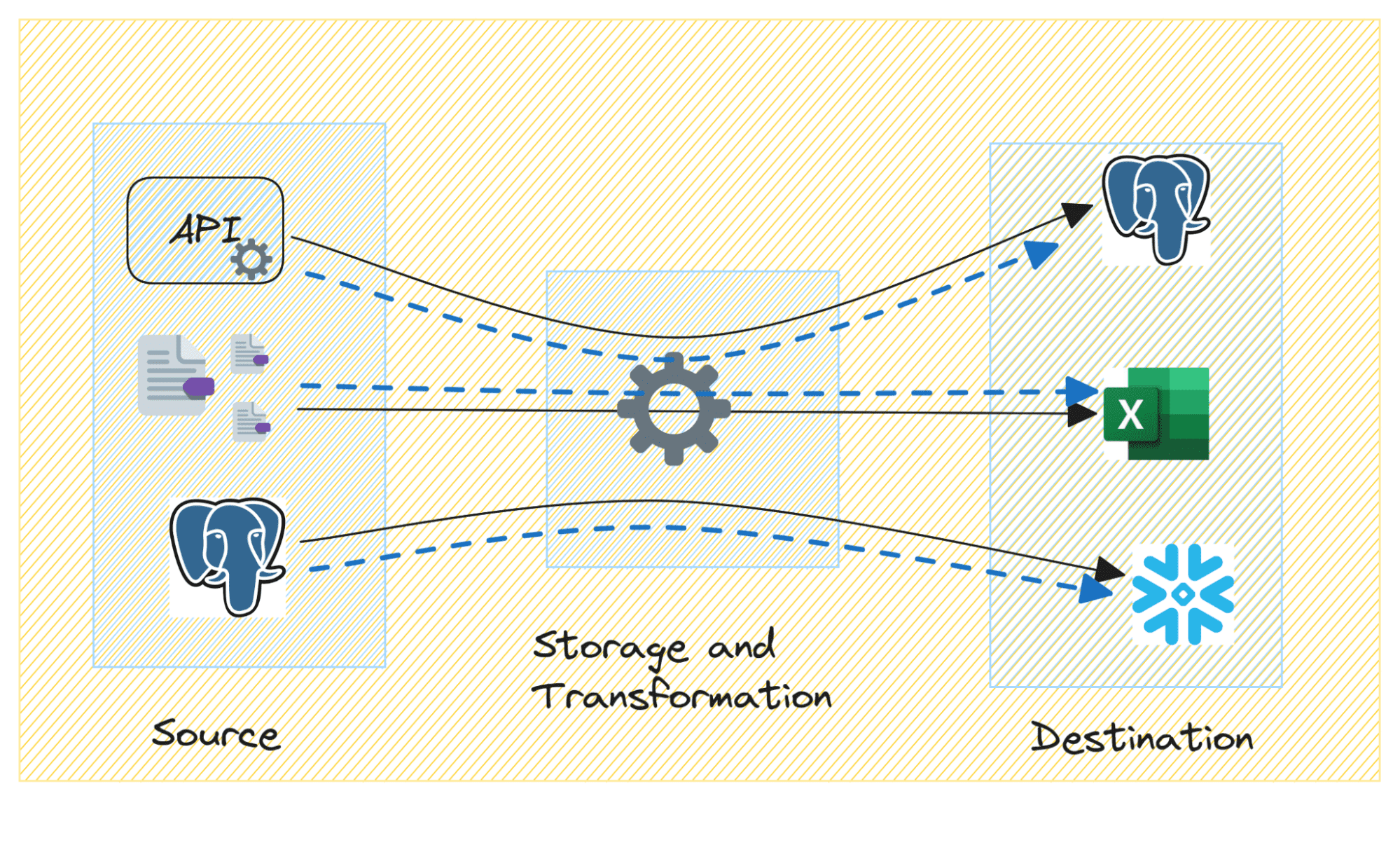
Image by Author
- Source Systems: This component focuses on the initial source of data. Such as databases, log files, sensors, applications, and other external sources.
- Metadata: Capturing metadata associated with the data is important as it includes details on data types, formats, and any business rules or constraints applied to the data.
- Data Movement and Transformation: Tracking ETL processes helps understand how data is extracted from source systems, undergoes diverse transformations, and is loaded into target systems.
- Destinations: Data lineage should also track the various intermediate and final destinations of the data, including databases, data warehouses, data lakes, and the like. It also includes other storage systems involved in processing and storing information. The final destination is generally the one where the processed data is stored for analysis or reporting.
In essence, data lineage provides a clear, holistic view of data flow, helping organizations understand dependencies and relationships. Because data lineage offers more than just a snapshot of data flow, it enables organizations to make informed decisions about data management and utilization.
Now that we know what data lineage is, let’s proceed to learn more on how and why it’s important.
Data Quality and Integrity
Data lineage helps in maintaining data quality by providing a transparent view of the data’s journey. This transparency ensures that data remains accurate, trustworthy, and aligned with business objectives.
Further, data lineage also helps mitigate data quality issues through lineage tracking. By tracing the flow of data (and its associated metadata), organizations can quickly identify and address data quality issues.
Regulatory Compliance
Data lineage assists organizations in meeting regulatory requirements by providing a comprehensive record of data movement, transformations, and storage. With clear visibility into the data’s journey from its source to destination along with the transformations, data lineage acts as a robust mechanism for ensuring adherence to legal and industry-specific regulations.
Troubleshooting and Debugging
Data lineage also helps identify and resolve data issues efficiently. It simplifies the process of troubleshooting by offering a guide to identify points of failure or inconsistencies. This accelerates the resolution of data-related issues, minimizing downtime and operational disruptions.
Data lineage also facilitates easier governance and improved overall efficiency amongst other advantages.
Impact Analysis
Data lineage is helpful in impact analysis by providing a clear view of how changes to data sources, structures, or processes will affect the overall system. This understanding is super helpful before implementing any modifications to avoid unintended consequences.
Data lineage also plays a role in making informed decisions and Managing Risks: A comprehensive understanding of how data is transformed and consumed, decision-makers can make informed choices about changes, updates, or implementations. This also ensures that potential risks are identified and mitigated before they can adversely affect the organization.
Auditing and Governance
Data governance relies on transparency and accountability. Data lineage serves as a foundational tool for enforcing governance policies, ensuring that data is handled in accordance with established standards, security protocols, and compliance requirements.
During audits, regulators and internal auditors often seek insights into data handling practices. Data lineage provides a detailed record of data movement, transformations, and storage, facilitating smooth audits and demonstrating adherence to regulatory requirements.
More Efficient Operation
By visualizing the flow of data, organizations can identify redundant processes, bottlenecks, or inefficiencies in their data workflows. Data lineage, therefore, helps eliminate unnecessary steps and optimizes the overall efficiency of data management.
Because data lineage provides a comprehensive yet better understanding of data flow: from data extraction to consumption, it also guides workflow optimizations to reduce processing times, optimize resource utilization, and more.
In summary, the applications of data lineage extend beyond its role as a tracking mechanism. It serves as a strategic tool for organizations to assess the impact of changes, maintain governance standards, and optimize operational efficiency.
As you might have guessed, data lineage can benefit from some level of automation. Because automated tools can continuously monitor data movement and transformations, providing real-time updates to data lineage, it ensures that the information is always current and reflective of the latest changes.
Some notable tools in the data lineage space include:
- Collibra: Includes robust data lineage features to visualize and understand the end-to-end journey of data.
- Informatica Axon: Part of the Informatica platform, Axon provides data governance and metadata management.
- IBM InfoSphere Information Governance Catalog: A tool for managing metadata and providing end-to-end data lineage tracking within complex enterprise environments.
- Apache Atlas: An open-source tool that offers comprehensive metadata management and data lineage capabilities, commonly used in big data ecosystems.
- Erwin Data Intelligence (DI): Offers a holistic view of data assets, including data lineage, to support data governance and compliance efforts.
In this article, we reviewed data lineage and its importance in ensuring data quality, compliance requirements, and more. Further, we discussed how tracing data lineage can help with impact analysis and optimizing the efficiency of the system.
Finally, we looked at some tools you can use to track data lineage. I hope you found this article helpful!
Bala Priya C is a developer and technical writer from India. She likes working at the intersection of math, programming, data science, and content creation. Her areas of interest and expertise include DevOps, data science, and natural language processing. She enjoys reading, writing, coding, and coffee! Currently, she’s working on learning and sharing her knowledge with the developer community by authoring tutorials, how-to guides, opinion pieces, and more.
[ad_2]
Source link